[Streamlit] Dashboard (2)구현
Dashboard 구현 :
앞서 Dashboard 를 설계했으니, streamlit 과 plotly 를 활용하여 Dashboard 를 실제로 구현해 보겠다.
1. streamlit 설치
- 가상환경 생성
- streamlit 배포 시 별도의 requirements.txt 를 넣어주어야 해당 라이브러리들이 streamlit share app 에 import 된다.
- 불필요한 라이브러리가 import 되는 것 방지하기 위해 별도의 가상 환경을 생성하는 것을 추천한다.
conda create -n streamlit python=3.8
conda activate streamlit
- 필요한 라이브러리 다운
- streamlit 은 pandas DataFrame 을 기준으로 시각화를 하기 때문에
pandas도 install 한다. - streamlit 에서 주로 사용할
plotly도 install 한다. - pip install streamlit 이 안 되면 python3 -m 을 붙이면 된다.
- streamlit 은 pandas DataFrame 을 기준으로 시각화를 하기 때문에
pip install streamlit
pip install pandas
pip install plotly
#python3 -m pip install streamlit
- streamlit 테스트
- 다음과 같은 명령어를 입력하면 아래 사진과 같이 8501 번 port 로 브라우저 창이 실행되는데 그러면 성공한 것이다.
streamlit hello
# python3 -m streamlit hello
- 파일 실행시키기
- 만약
streamlit.py라는 파일명에 코드를 작성했다면 아래와 같이 실행시켜주면 웹 페이지가 실행된다.
- 만약
streamlit run streamlit.py
2. 데이터 불러오기
- Redis Cluster 라이브러리 설치
pip install redis-py-cluster
- 필요한 모듈 import
from rediscluster import RedisCluster
import time
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
import plotly.express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
- Redis Cluster 와 연결
redis_nodes = [{'host': 'cluster ip', 'port': '6300'},
{'host': 'cluster ip', 'port': '6301'},
{'host': 'cluster ip', 'port': '6302'}]
redis_password = 'redis cluster 접근 비밀번호'
client = RedisCluster(startup_nodes=redis_nodes,
password=redis_password,
decode_responses=True)
- 불러올 데이터 기준
- Redis 에서 당일 로그 데이터만 조회하기 때문에 당일 날짜를 date 변수에 yyyyMMdd 형태로 저장한다.
- ex. 2022년 12월 20일 > 20221220
date = time.strftime('%Y%m%d', time.localtime(time.time()))
- 공통 집계 데이터 DataFrame 형태로 변환
- Redis 에 문자열 타입으로 저장된 숫자들을 숫자 type 으로 변환한다.
pd.to_numeric(errors='ignore')- 숫자 type 으로 변경 불가능한 열을 만나면 에러가 발생한다.
- 위 에러를 무시하도록 하는 속성이
errors='ignore'이다.
- Redis 에 문자열 타입으로 저장된 숫자들을 숫자 type 으로 변환한다.
# ------ common data
rows = list()
for key in client.scan_iter(match=f'common:{date}:*', count=100):
temp, splitted = dict(), key.split(':')
temp['date'], temp['hour'] = splitted[1], splitted[2]
temp['user_gender'], temp['user_age'], temp['user_region'] = splitted[3], splitted[4], splitted[5]
temp.update(client.hgetall(key))
rows.append(temp)
df = pd.DataFrame(rows)
df = df.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='ignore')
print(df.head())
date hour user_gender ... ecopoint1_click save_ecopoint1 login
0 20221220 20 W ... 2 20 0
1 20221220 20 none ... 0 0 3
2 20221220 17 W ... 2 100 1
3 20221220 15 W ... 0 0 1
4 20221220 13 M ... 2 100 2
- 무라벨 제품 검색 데이터 DataFrame 형태로 변환
# ------ search data
rows = list()
for key in client.scan_iter(match=f'search:{date}:*', count=100):
temp, splitted = dict(), key.split(':')
temp['date'], temp['user_gender'], temp['user_age'] = splitted[1], splitted[2], splitted[3]
temp['search_word'], temp['count'] = splitted[4], int(client.hget(key, 'count'))
rows.append(temp)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(rows)
df2 = df2.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='ignore')
print(df2)
date user_gender user_age search_word count
0 20221220 M 20 사이다 2
1 20221220 W 30 사이다 1
2 20221220 M 20 홍차 1
3 20221220 W 30 생수 1
4 20221220 M 20 헛개수 1
3. 기본 설정
다음과 같이 페이지 제목과 아이콘을 설정한다.
# ------------ base
st.set_page_config(page_title="Ciaolabella Dashboard",
page_icon=":bar_chart:",
layout="wide")
st.write(f'# DATE : {date}')
4. 데이터 필터 생성 및 데이터 필터링
특정 시간대, 연령대, 성별, 지역 관련 데이터만 시각화해서 보여줄 수 있도록 필터 sidebar를 추가하고 df.query() 를 통해 선택한 특성에 맞는 데이터만 불러온다.
# ------------ data filter
st.sidebar.header("Filter")
hour = st.sidebar.multiselect(
"Select Hour:",
options=df['hour'].unique(),
default=df['hour'].unique()
)
age = st.sidebar.multiselect(
"Select Age:",
options=df['user_age'].unique(),
default=df['user_age'].unique()
)
gender = st.sidebar.multiselect(
"Select Gender:",
options=df['user_gender'].unique(),
default=df['user_gender'].unique()
)
region = st.sidebar.multiselect(
"Select Region:",
options=df['user_region'].unique(),
default=df['user_region'].unique()
)
selected = df.query(
"hour == @hour & user_age == @age & user_gender == @gender & user_region == @region"
)
selected2 = df2.query(
"user_age == @age & user_gender == @gender"
)
5. 레이아웃 생성
with tab:구문 안에서 해당하는 그래프들을with item:구문 안에 넣어주면 된다.
# ------------ make tabs
tab1, tab2, tab3, tab4 = st.tabs(["IN OUT", "MENU", "ECO POINT", "NO LABEL"])
# ------------ tab1 : login and logout
with tab1:
item1, item2, item3 = st.columns(3)
st.markdown("---")
item4, item5, item6 = st.columns([1,1,1])
# ------------ tab2 : menu click
with tab2:
item1, item2 = st.columns(2)
st.markdown('#### 메뉴 가수요 대비 실수요 (%)')
item3, item4 = st.columns(2)
item5, item6 = st.columns(2)
# ------------ tab3 : ecopoint service
with tab3:
item1, item2 = st.columns(2)
item3, item4 = st.columns(2)
# ------------ tab4 : nolabel service
with tab4:
item1, item2, item3 = st.columns(3)
- 필터링한 데이터를 직접 확인하고 csv 확장자로 다운로드하는 기능도 추가한다.
# ------------ data download
st.markdown("---")
st.markdown('#### 🔻 Common 데이터 확인 및 다운로드')
with st.expander("Click Here"):
st.write(selected)
st.download_button(
label="Download .csv",
data=selected.to_csv().encode('utf-8'),
file_name=f'ciaolabella_common_{date}.csv',
mime='text/csv'
)
st.markdown('#### 🔻 Search 데이터 확인 및 다운로드')
with st.expander("Click Here"):
st.write(selected2)
st.download_button(
label="Download .csv",
data=selected2.to_csv().encode('utf-8'),
file_name=f'ciaolabella_search_{date}.csv',
mime='text/csv'
)
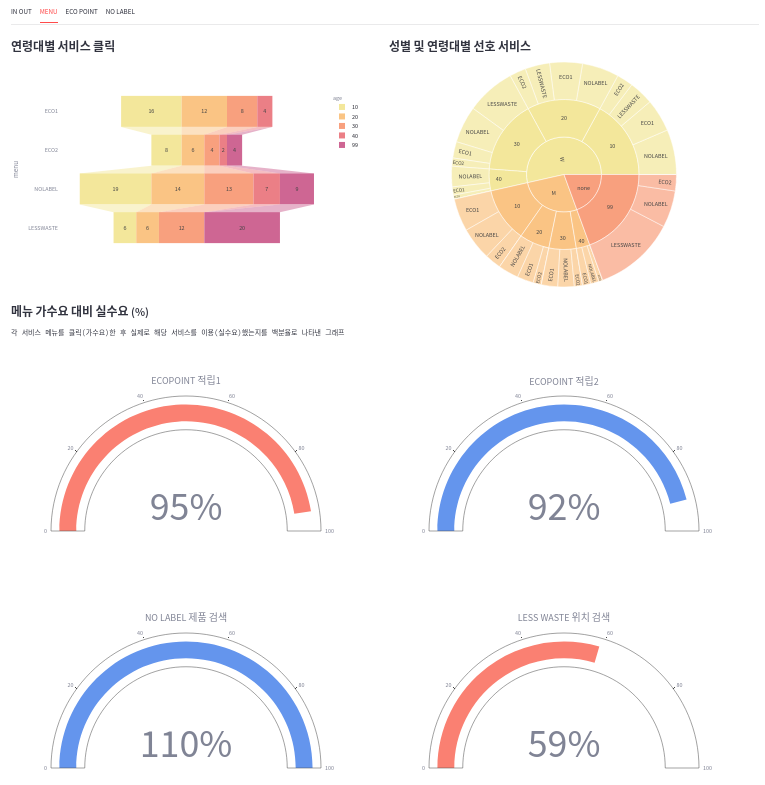
- 아래는 tab3 의 완성된 레이아웃이다.
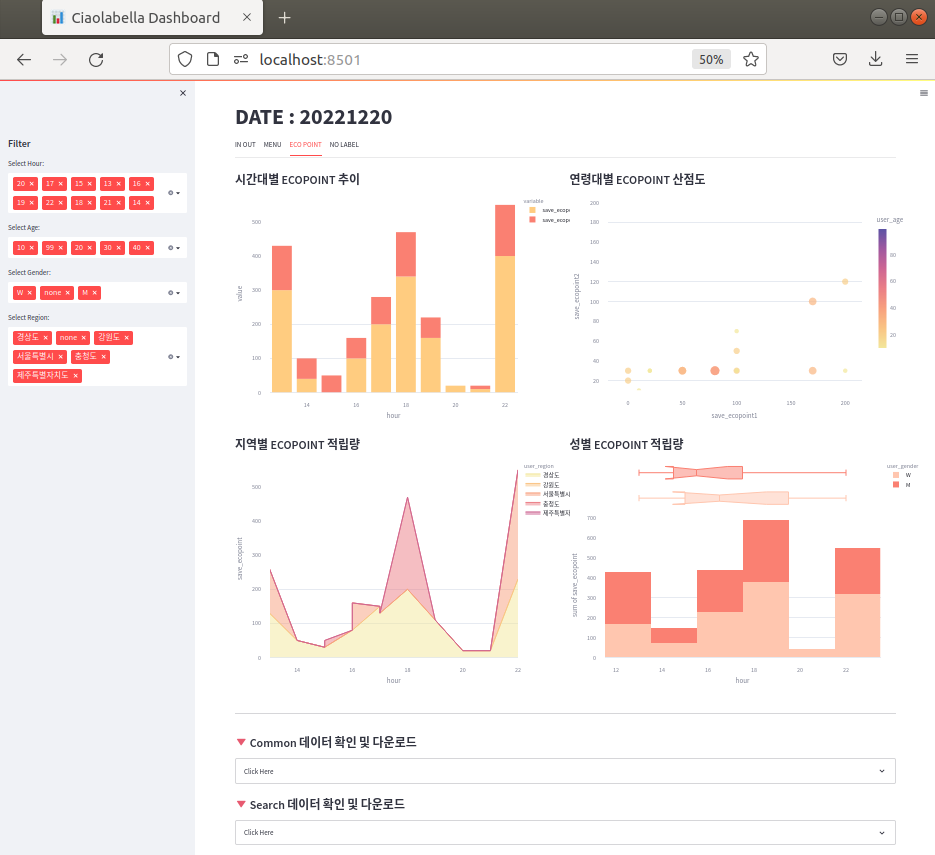
6. 시각화
6.1. IN OUT
1) tab1
- 로그인 및 로그아웃 관련 시각화 tab1 은 다음과 같이 구현하였다.
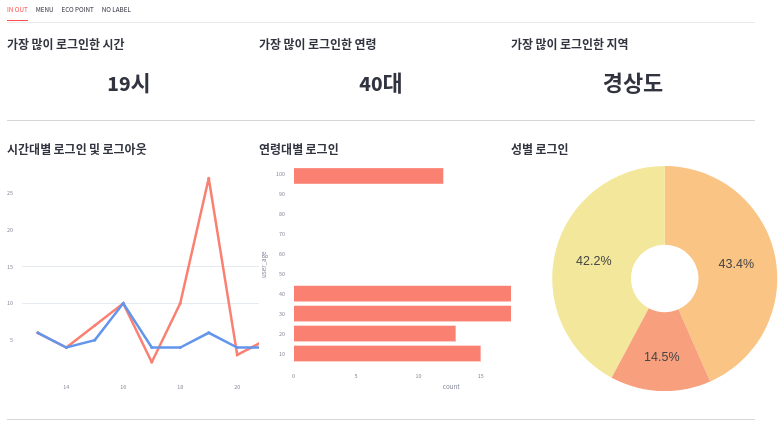
2) tab1 의 item1, item2, item3
- 가장 많이 로그인한 시간대 / 연령대 / 지역
most_login_hour = (selected.groupby("hour")["login"].sum().sort_values().index[-1])
most_login_age = (selected.groupby("user_age")["login"].sum().sort_values().index[-1])
most_login_region = (selected.groupby("user_region")["login"].sum().sort_values().index[-1])
with item1:
st.markdown("#### 가장 많이 로그인한 시간")
st.markdown(f"# <div style='text-align: center;'>{most_login_hour}시 </div>", unsafe_allow_html=True)
with item2:
st.markdown("#### 가장 많이 로그인한 연령")
st.markdown(f"# <div style='text-align: center;'>{most_login_age}대 </div>", unsafe_allow_html=True)
with item3:
st.markdown("#### 가장 많이 로그인한 지역")
st.markdown(f"# <div style='text-align: center;'>{most_login_region} </div>", unsafe_allow_html=True)
3) tab1 의 item4
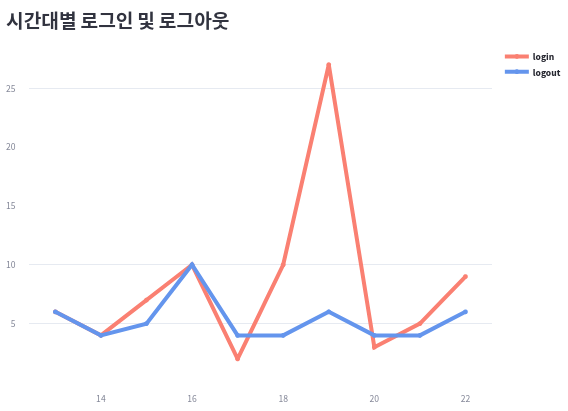
inout_by_hour = (
selected.groupby(by=["hour"])[["login", "logout"]].sum().sort_index()
)
print(inout_by_hour.head(6))
---
login logout
hour
13 6 6
14 4 4
15 7 5
16 10 10
17 2 4
18 10 4
line1 = go.Figure()
line1.add_trace(go.Scatter(
x=inout_by_hour.index,
y=inout_by_hour["login"],
name='<b>login</b>',
line=dict(color='Salmon', width=5),
))
line1.add_trace(go.Scatter(
x=inout_by_hour.index,
y=inout_by_hour["logout"],
name='<b>logout</b>',
line=dict(color='CornflowerBlue', width=5),
))
line1.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=10, r=10, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(line1)
4) tab1 의 item5
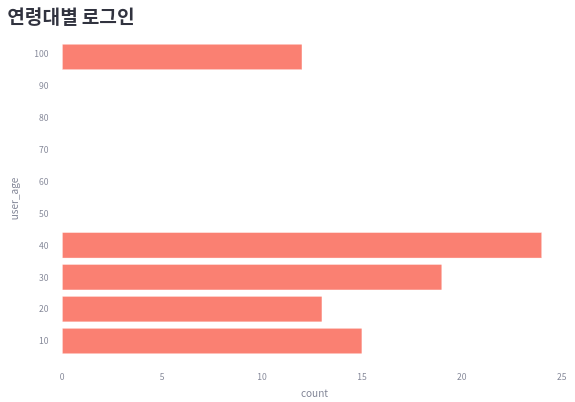
login_by_age = (
selected.groupby(by=["user_age"])["login"].sum().sort_index()
)
print(login_by_age)
---
user_age
10 15
20 13
30 19
40 24
99 12
bar1 = px.bar(
login_by_age,
x=login_by_age.values,
y=login_by_age.index,
# color_discrete_sequence=['#0083B8'] * len(eco1_by_hour),
color_discrete_sequence=["Salmon"],
template='plotly_white',
orientation='h',
labels={'x': 'count'}
)
bar1.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(bar1)
5) tab1 의 item6
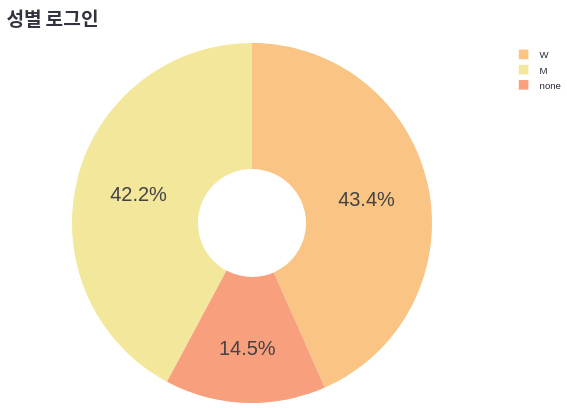
login_by_gender = (
selected.groupby(by=["user_gender"])["login"].sum()
)
print(login_by_gender)
---
user_gender
M 35
W 36
none 12
pie1 = go.Figure(go.Pie(
labels=login_by_gender.index,
values=login_by_gender.values,
hole=.3,
marker_colors=px.colors.sequential.Sunset
))
pie1.update_layout(
margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0),
font = dict(family="Arial", size=25, color="#000000")
)
st.plotly_chart(pie1)
6.2. MENU
1) tab2
- 메뉴(서비스) 이용 관련 시각화 tab2 은 다음과 같이 구현하였다.
2) tab2 의 item1
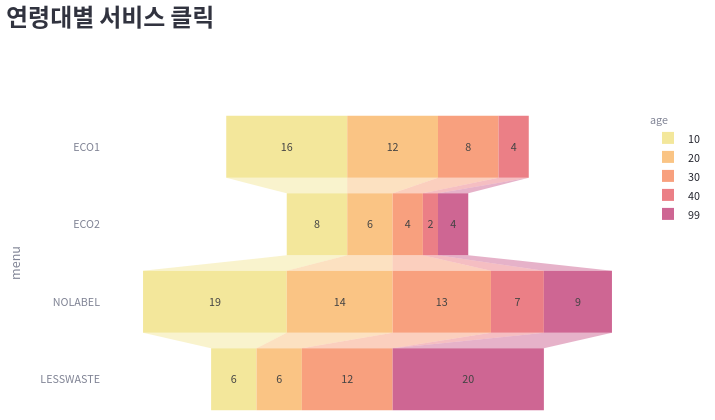
menu_by_age = (
selected[["user_age", "menu_eco1", "menu_eco2", "menu_nolabel", "menu_lesswaste"]].groupby(
by=["user_age"]).sum()
).stack().reset_index()
menu_by_age.columns = ["age", "menu", "click"]
menu_by_age["menu"] = menu_by_age["menu"].apply(lambda x: x.split('_')[1].upper())
print(menu_by_age.head(10))
---
age menu click
0 10 ECO1 16
1 10 ECO2 8
2 10 NOLABEL 19
3 10 LESSWASTE 6
4 20 ECO1 12
5 20 ECO2 6
6 20 NOLABEL 14
7 20 LESSWASTE 6
8 30 ECO1 8
9 30 ECO2 4
funnel1 = px.funnel(
menu_by_age,
x='click',
y='menu',
color='age',
color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.sequential.Sunset
)
st.plotly_chart(funnel1)
3) tab2 의 item2
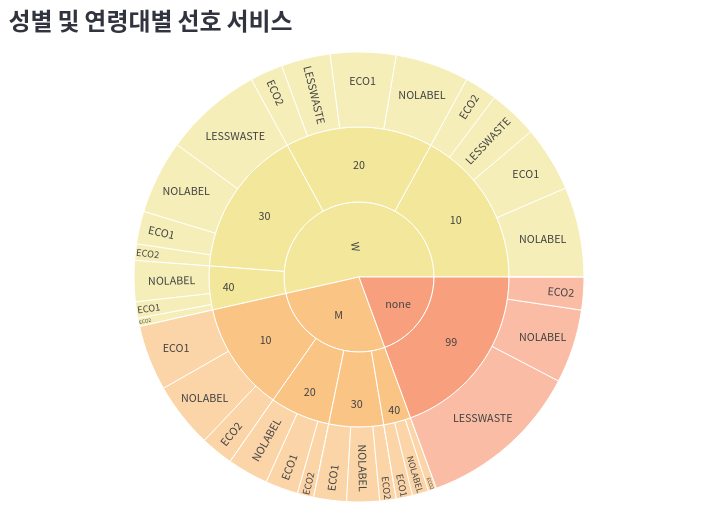
menu_by_gender_age = (
selected[["user_gender", "user_age", "menu_eco1", "menu_eco2", "menu_nolabel", "menu_lesswaste"]]\
.groupby(by=["user_gender", "user_age"]).sum()
).stack().reset_index()
menu_by_gender_age.columns = ["gender", "age", "menu", "click"]
menu_by_gender_age["menu"] = menu_by_gender_age["menu"]\
.apply(lambda x: x.split('_')[1].upper())
print(menu_by_gender_age.head())
---
gender age menu click
0 M 10 ECO1 8
1 M 10 ECO2 4
2 M 10 NOLABEL 8
3 M 10 LESSWASTE 0
4 M 20 ECO1 4
...
16 W 10 ECO1 8
17 W 10 ECO2 4
18 W 10 NOLABEL 11
19 W 10 LESSWASTE 6
20 W 20 ECO1 8
...
31 W 40 LESSWASTE 0
32 none 99 ECO1 0
33 none 99 ECO2 4
34 none 99 NOLABEL 9
35 none 99 LESSWASTE 20
sunburst1 = px.sunburst(
menu_by_gender_age,
path=["gender", "age", "menu"],
values="click",
color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.sequential.Sunset
)
sunburst1.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(sunburst1)
4) tab2 의 item3
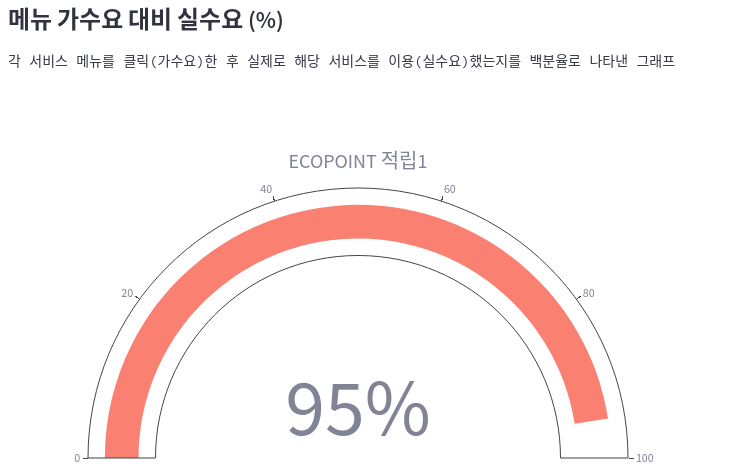
eco1_demand = selected['ecopoint1_click'].sum() / selected['menu_eco1'].sum()
print(eco1_demand)
---
0.95
gauge1 = go.Figure(go.Indicator(
title={"text": "ECOPOINT 적립1"},
value=round(eco1_demand * 100),
number={"suffix": "%"},
mode="gauge+number",
gauge={
"axis": {"range": [None, 100]},
"bar": {"color": "Salmon"}
}
))
st.plotly_chart(gauge1)
5) tab2 의 item4, item5, item6
- 나머지 item 도 item3 과 같은 코드에 eco1_demand 변수 대신 다음과 같은 변수들로 변경해서 넣어주면 된다.
eco2_demand = selected['ecopoint2_click'].sum() / selected['menu_eco2'].sum()
nolabel_demand = selected['nolabel_click'].sum() / selected['menu_nolabel'].sum()
lesswaste_demand = selected['lesswaste_click'].sum() / selected['menu_lesswaste'].sum()
6.3. ECOPOINT
1) tab3
- ECOPOINT 적립 관련 시각화 tab3 은 다음과 같이 구현하였다.
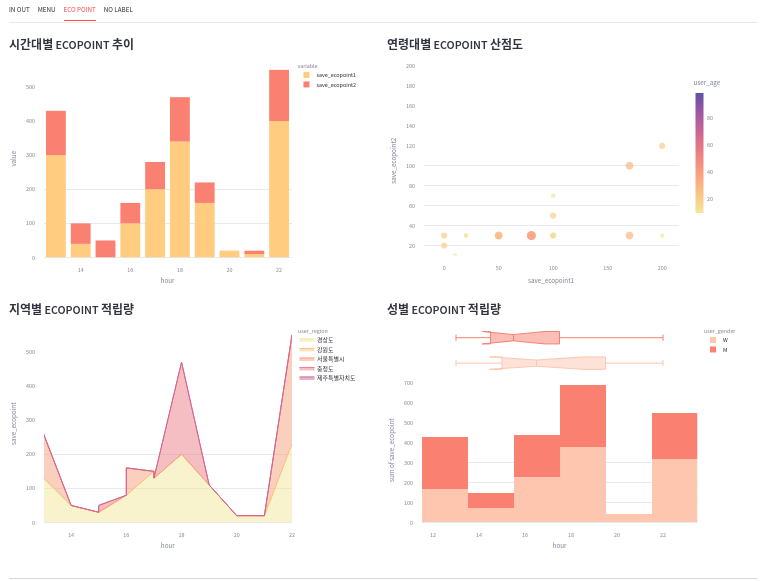
2) tab3 의 item1
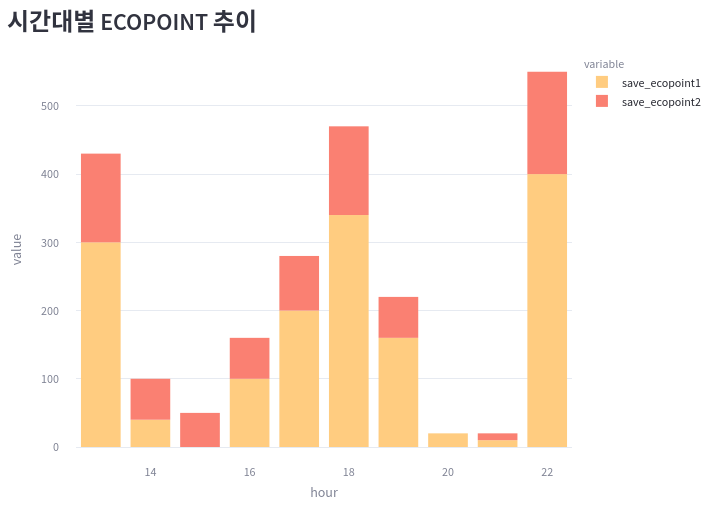
ecopoint_by_hour = selected[["hour", "save_ecopoint1", "save_ecopoint2"]]\
.groupby(by=["hour"]).sum()
print(ecopoint_by_hour.head())
---
save_ecopoint1 save_ecopoint2
hour
13 300 130
14 40 60
15 0 50
16 100 60
17 200 80
bar2 = px.bar(
ecopoint_by_hour,
x=ecopoint_by_hour.index,
y=["save_ecopoint1", "save_ecopoint2"],
color_discrete_sequence=["#FFCC80", "Salmon"],
)
bar2.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(bar2)
3) tab3 의 item2
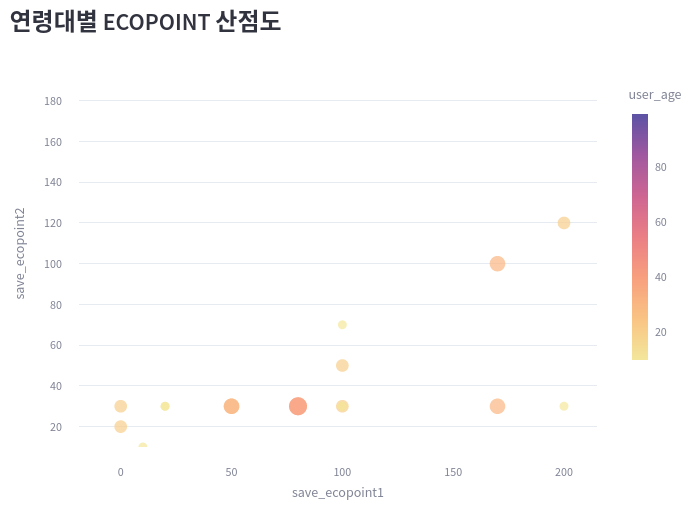
ecopoint_by_age = selected[["user_age", "save_ecopoint1", "save_ecopoint2"]]
ecopoint_by_age["user_age"] = ecopoint_by_age["user_age"].astype("int")
print(ecopoint_by_age.head(6))
---
user_age save_ecopoint1 save_ecopoint2
0 10 20 0
1 99 0 0
2 20 100 50
3 30 0 0
4 10 100 30
5 20 0 30
bubble1 = px.scatter(
selected[["user_age", "save_ecopoint1", "save_ecopoint2"]],
x="save_ecopoint1",
y="save_ecopoint2",
size="user_age",
color="user_age",
color_continuous_scale=px.colors.sequential.Sunset
)
bubble1.update_layout(yaxis_range=[10, 200], margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(bubble1)
4) tab3 의 item3
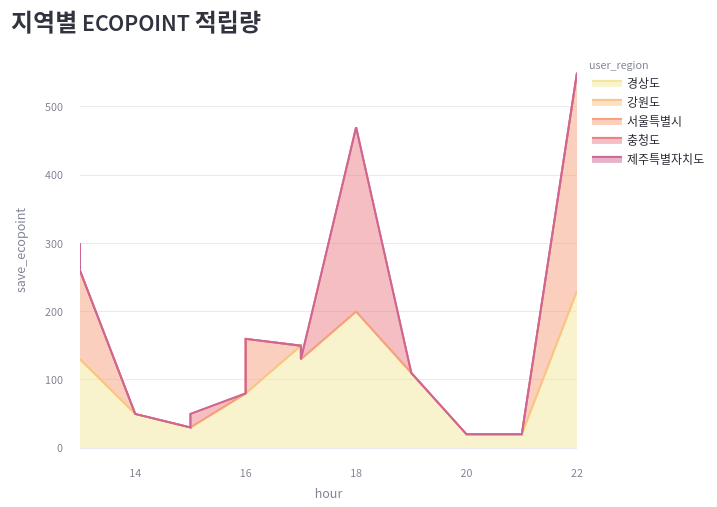
ecopoint_by_region = selected[selected["user_gender"]!="none"]
ecopoint_by_region["save_ecopoint"] = ecopoint_by_region["save_ecopoint1"] + ecopoint_by_region["save_ecopoint2"]
print(ecopoint_by_region.head())
---
date hour user_gender ... save_ecopoint1 login save_ecopoint
0 20221220 20 W ... 20 0 20
2 20221220 17 W ... 100 1 150
3 20221220 15 W ... 0 1 0
4 20221220 13 M ... 100 2 130
5 20221220 15 M ... 0 2 30
area1 = px.area(
ecopoint_by_region,
x="hour",
y="save_ecopoint",
color="user_region",
color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.sequential.Sunset,
)
area1.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(area1)
5) tab3 의 item4
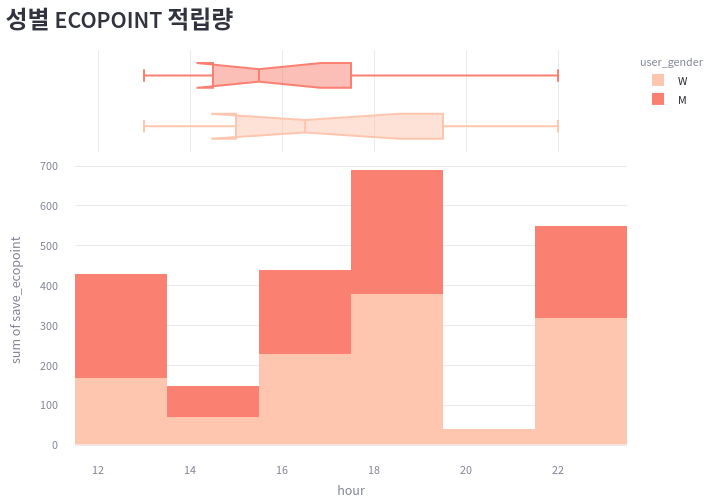
ecopoint_by_gender = ecopoint_by_region
hist1 = px.histogram(
ecopoint_by_gender,
x="hour",
y="save_ecopoint",
color="user_gender",
marginal="box",
color_discrete_sequence=["#FFC6AF", "Salmon"],
hover_data=selected.columns
)
hist1.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(hist1)
6.4. NO LABEL
1) tab4
- 무라벨 제품 검색 관련 시각화 tab4 은 다음과 같이 구현하였다.
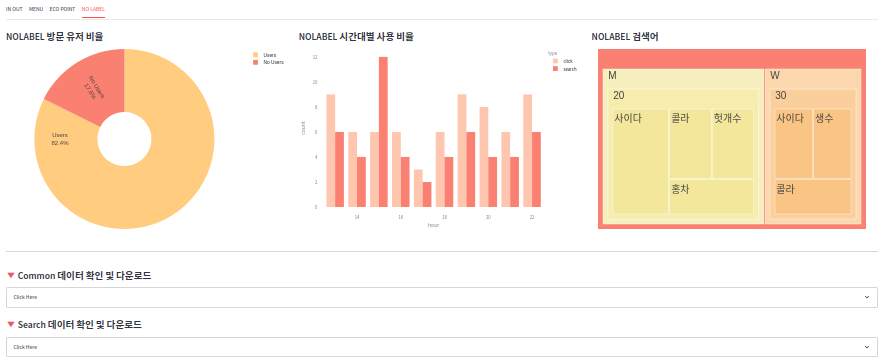
2) tab4 의 item1
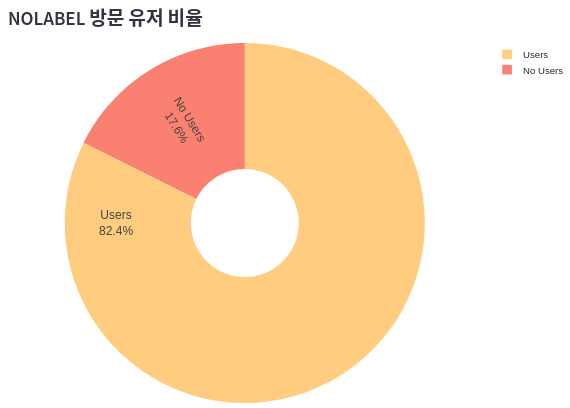
condition = selected['user_gender'] == 'none'
nouser = sum(selected.loc[condition].nolabel_click)
user = sum(selected.loc[~condition].nolabel_click)
print(nouser)
print(user)
---
12
56
pie2 = go.Figure(go.Pie(
labels=["Users", "No Users"],
values=[user, nouser],
textinfo='label+percent',
insidetextorientation='radial',
hole=.3,
marker_colors=["#FFCC80", "Salmon"],
))
pie2.update_layout(
margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0),
font=dict(family="Arial", size=15, color="#000000")
)
st.plotly_chart(pie2)
3) tab4 의 item2
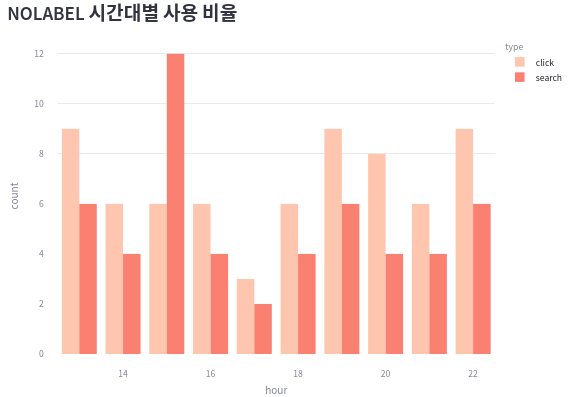
click_search = (
selected[["hour", "nolabel_click", "nolabel_search"]].groupby(by=["hour"]).sum()
).stack().reset_index()
click_search.columns = ["hour", "type", "count"]
click_search["type"] = click_search["type"].apply(lambda x: x.split("_")[1])
print(click_search)
---
hour type count
0 13 click 9
1 13 search 6
2 14 click 6
3 14 search 4
4 15 click 6
5 15 search 12
bar3 = px.bar(
click_search,
x="hour",
y="count",
color="type",
color_discrete_sequence=["#FFC6AF", "Salmon"],
barmode="group"
)
bar3.update_layout(margin=dict(t=0, l=0, r=0, b=0))
st.plotly_chart(bar3)
4) tab4 의 item3
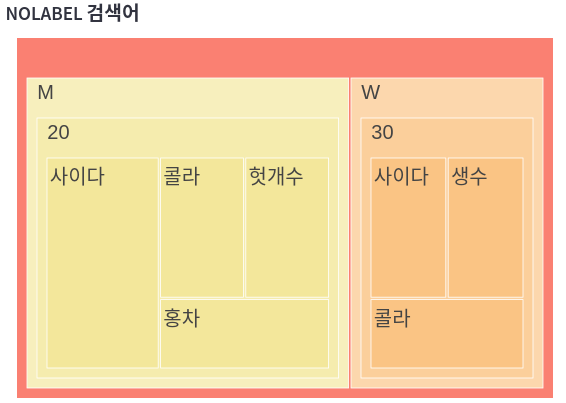
print(selected2)
---
date user_gender user_age search_word count
0 20221220 M 20 사이다 2
1 20221220 W 30 사이다 1
2 20221220 M 20 홍차 1
3 20221220 W 30 생수 1
4 20221220 M 20 헛개수 1
5 20221220 W 30 콜라 1
6 20221220 M 20 콜라 1
tree1 = px.treemap(
selected2,
path=['user_gender', 'user_age', 'search_word'],
values='count',
color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.sequential.Sunset,
)
tree1.update_traces(
root_color="Salmon"
)
tree1.update_layout(
margin=dict(t=0, l=15, r=15, b=0),
font=dict(family="Arial", size=25, color="#000000")
)
st.plotly_chart(tree1)
REFERENCES
- plotly 차트 참고
- plotly 색상 참고
- color list 참고
- 이모티콘 참고
